LeetCode记录①
在LeetCode学习的记事本。

141. 判断一个链表是否含有环形结构
141.Linked List Cycle
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer
poswhich represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. Ifposis-1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
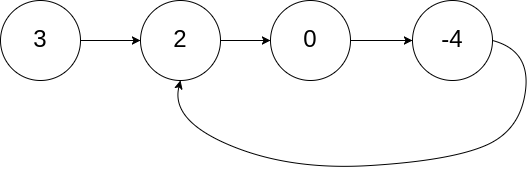
解题思路
使用hash表存储访问过的节点,如果发现节点已经在表中,则表示链表含有环形结构。
使用快慢指针,当快指针与慢指针相遇时,表示链表中存在环形结构。
代码
java
1 | //141 hashSet方式 |
golang
1 | //141 map方式 存储的K是节点地址 v可以是任意值 |
142. 找出链表中环结构的起点
142.Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return
null.To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer
poswhich represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. Ifposis-1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.Note: Do not modify the linked list.

解题思路
使用hash表存储访问过的节点,返回第一个与表中重复的节点。
使用快慢指针,当快指针与慢指针相遇时,相遇点与环形结构起点的距离,刚好等于
head链表头节点到环形结构起点的距离。利用这一点,在第一次相遇时,让快指针再次从head开始,以与慢指针同样的速度前进,同时慢指针继续从相遇点原速前进,则接下来的相遇点即为所求的环形结构起点。- 这样说可能有些抽象,我下面画图说明:
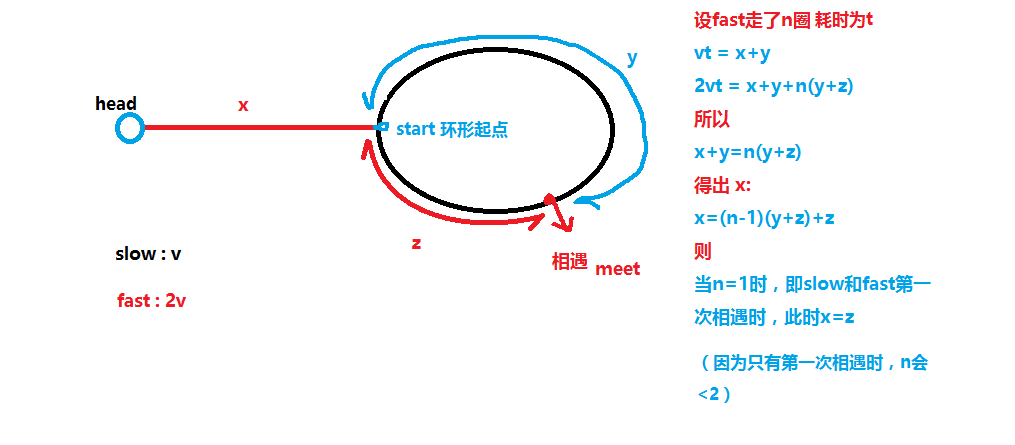
假设有两个运动员
slow和fast,slow的速度为v,fast的速度是slow的2倍为2v,两人从head点开始通过一段长为x的直道,最后进入环形跑道做匀速运动,设两人相遇点为meet处,设环形跑道的周长C为y+z,可以得出x=kC+z,其中k为自然数。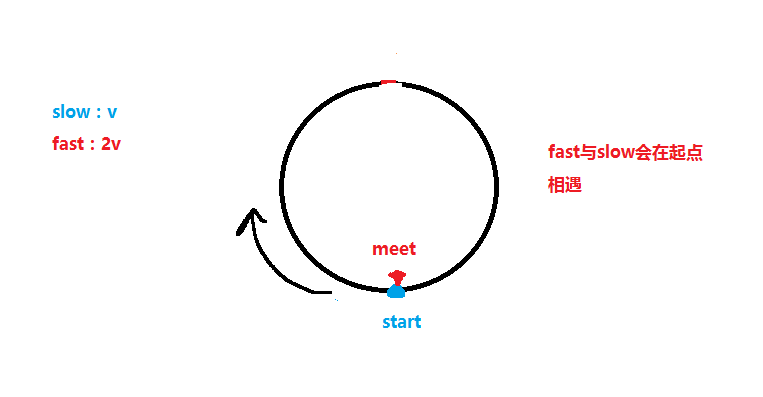
如果没有直道,相遇点就会一直是起点,也可以说明上面的推论是正确的。
代码
java
1 | //142 hashSet方式略 |
golang
1 | //142 hash表方式略 |
78. 找出一个集合的所有子集
78.Subsets
Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Example:
1 | Input: nums = [1,2,3] |
解题思路
迭代,从每轮子集中寻找规律
结果集初始为
{},第一轮为{},{1},第二轮为{},{1},{2},{1,2},可以得出:每轮结果都是对上一轮中所有集合的扩充。对所有上轮集合都添加1个当前元素,然后把此轮得到的集合,合并到结果集。将结果集命名为
allList,我在下图解释了第二轮集合的获取方式: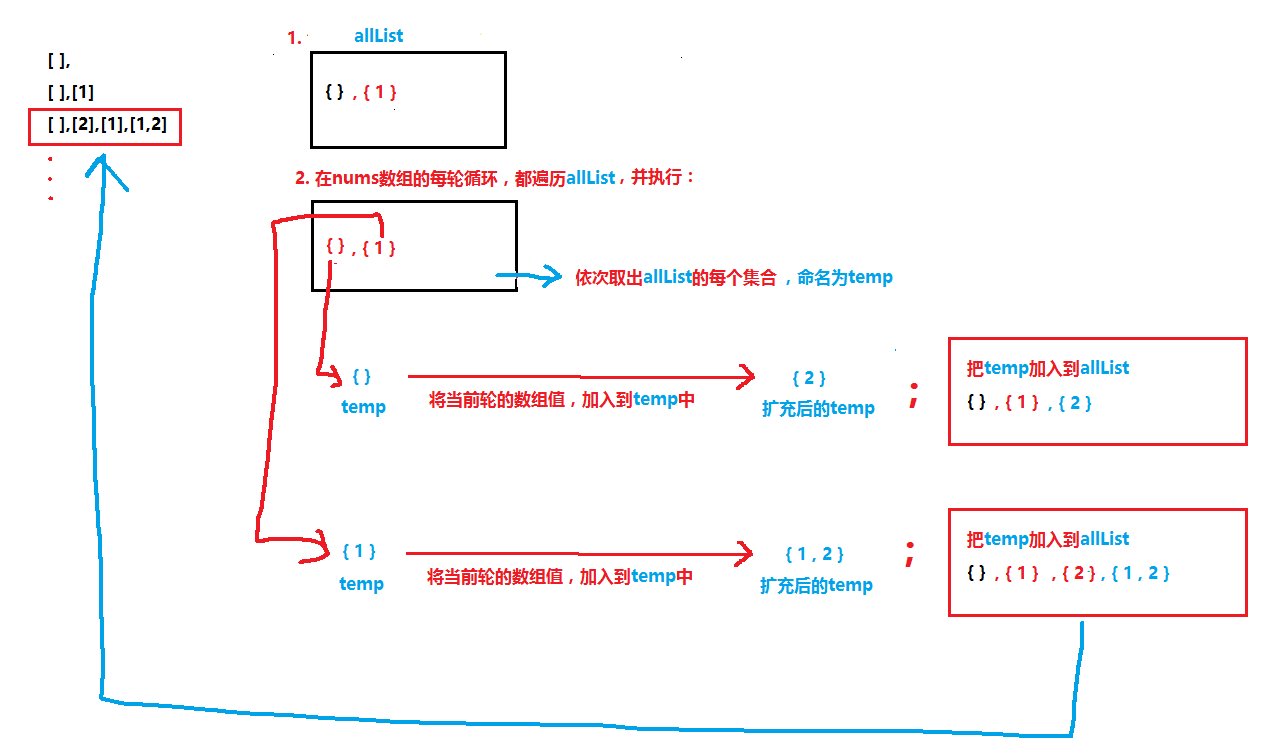
递归回溯,常用的方法,我在90题也使用了同样的方法。
代码
java
1 | //78. 迭代方式 |
golang
1 | //78 迭代方式 |
349. 两个数组的交集
349.Intersection of Two Arrays
Given two arrays, write a function to compute their intersection.
Example:
1 | Input: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4] |
这题应该是考集合的使用,使用set或者map都是可以的,第350题也大致相同。
java
1 | //349. Intersection of Two Arrays |
golang
1 | //349. Intersection of Two Arrays |